(Bold text = submission by CCAP staff or collaborators)
Note: for strains where we have DNA barcodes we can be reasonably confident of identity, however for those not yet sequenced we rely on morphology
and the original identification, usually made by the depositor. Although CCAP makes every effort to ensure the correct taxonomic identity of strains, we cannot guarantee
that a strain is correctly identified at the species, genus or class levels. On this basis users are responsible for confirming the identity of the strain(s) they receive
from us on arrival before starting experiments.
For strain taxonomy we generally use AlgaeBase for algae and
Adl et al. (2019) for protists.
| Attributes | |
| Authority | Thuret 1863 |
| Isolator | Gachon (2006) |
| Collection Site | intertidal Dunstaffnage, Oban, Scotland, UK |
| Climatic Zone | Temperate |
| Notes | Isolation: clonal isolate obtained from an originally Eurychasma-infected Ectocarpus plant; Transferred into new liquid medium every 6 months. Might be grown on agar 1/2 strength Provasoli medium to decrease transfer frequency. If used for Eurychasma inoculation, it must have been grown for 2-3 weeks in liquid medium; This macroalgal culture contains bacteria and probably other organisms in low numbers, we are happy to provide further info on specific strains if you contact us |
| Axenicity Status | Bacteria and other organisms present |
| Area | Europe |
| Country | UK |
| Environment | Marine |
| GMO | No |
| Group | Macroalgae |
| In Scope of Nagoya Protocol | No |
| ABS Note | Collected pre Nagoya Protocol. No known Nagoya Protocol restrictions for this strain. |
| Collection Date | c 2006 |
| Original Designation | Ectocarpus Oban 06-29-7 |
| Pathogen | Not pathogenic: Hazard Class 1 |
| Strain Maintenance Sheet | SM_Ectocarpus.pdf |
| Toxin Producer | Not Toxic / No Data |
| Type Culture | No |
| Taxonomy WoRMS ID | 496828 |
| Formerly Listed in CCAP as | Ectocarpus sp. |
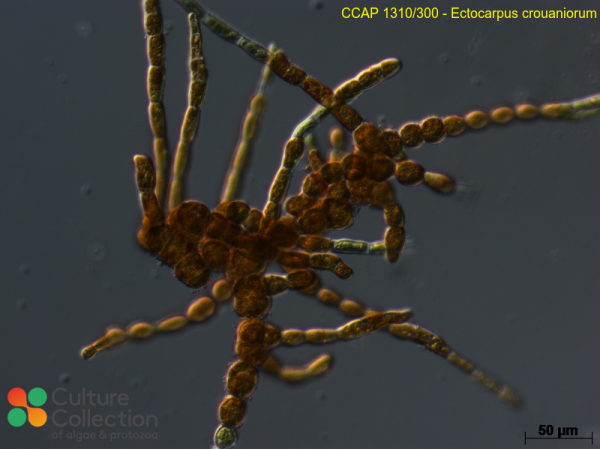
CCAP 1310/300
Ectocarpus crouaniorum
- Product Code: CCAP 1310/300
- Availability: See Availability/Lead Times