Note: for strains where we have DNA barcodes we can be reasonably confident of identity, however for those not yet sequenced we rely on morphology
and the original identification, usually made by the depositor. Although CCAP makes every effort to ensure the correct taxonomic identity of strains, we cannot guarantee
that a strain is correctly identified at the species, genus or class levels. On this basis users are responsible for confirming the identity of the strain(s) they receive
from us on arrival before starting experiments.
For strain taxonomy we generally use AlgaeBase for algae and
Adl et al. (2019) for protists.
| Attributes | |
| Authority | Kützing emend. Elenkin 1924 |
| Isolator | Gerloff (1948) |
| Collection Site | Lake Mendota, Madison, Wisconsin, USA |
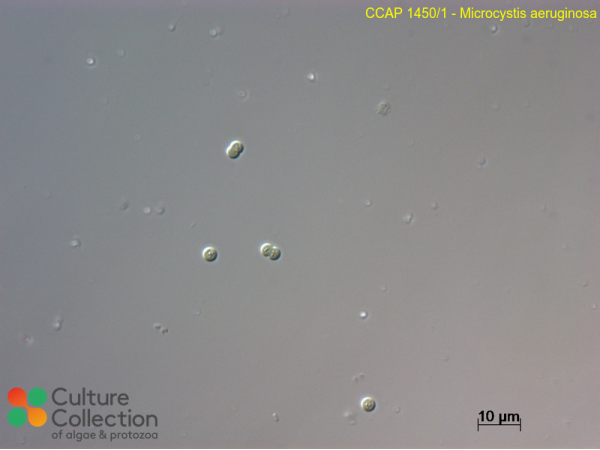
| Notes | unicellular; LC-MS analysis by RGU in 2021 for cylindrospermopsins, microcystins and anatoxins: None Detected. |
| Axenicity Status | Bacteria present |
| Area | North America |
| Country | USA |
| Environment | Freshwater |
| GMO | No |
| Group | Cyanobacteria |
| Original Designation | 1036 |
| Pathogen | Not pathogenic: Hazard Class 1 |
| Strain Maintenance Sheet | SM_FreshwaterCyanobacteria.pdf |
| Toxin Producer | Not Toxic / No Data |
| Type Culture | No |
| Taxonomy WoRMS ID | 146558 |
| Equivalent Strains | ATCC 27153,PCC 7005,UTCC 73,UTEX 2061 |
CCAP 1450/1
Microcystis aeruginosa
- Product Code: CCAP 1450/1
- Availability: See Availability/Lead Times
Related Products
CCAP FAJM-C
Jaworski's Medium (JM)
CONCENTRATED STOCKS
Non-sterile concentrated stocks to make up 5 litres of JM medium. Jaworski's Medium is used for cul
CCAP FAJM-P
Jaworski's Medium (JM)
1 LITRE PREMADE
1 litre of sterile, ready to use, JM medium. Jaworski's Medium is used for culturing freshwater alg
CCAP FAJMSE-P
JM:SE Medium
1 LITRE PREMADE
1 litre of sterile, ready to use, JM:SE medium (a 7:3 mix of JM and SE2 media). JM:SE medium is use